Circuit analysis Tutorial
AKNM Circuit Magic- circuit analysis software
Norton & Thevenin equivalent
Thévenin's Theorem
Any voltage network which may be viewed from two terminals can be replaced by a
voltage-source equivalent circuit comprising a single voltage source E and a single
series resistance R.. The voltage V is the open-circuit voltage between the two terminals and
the resistance Z is the resistance of the network viewed from the terminals with all
voltage sources removed from circuit.
Sample


All circuits are
equivalent. Resistors R1,R2, R3 and voltage source are transformed into Requ
Eequ,
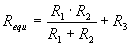 see parallel, series
simplifications.
see parallel, series
simplifications.
To determine Eequ we shall break off branch connecting node 1 and node 2


Norton's Theorem
Any current network which may be viewed from two terminals can be replaced by a
current-source equivalent circuit comprising a single current source I and a single
shunt conductance G. The current I is the
short-circuit current between the two terminals and the conductance G is the conductance of the network viewed from the terminals with all branches
containing current sources are broken off.







